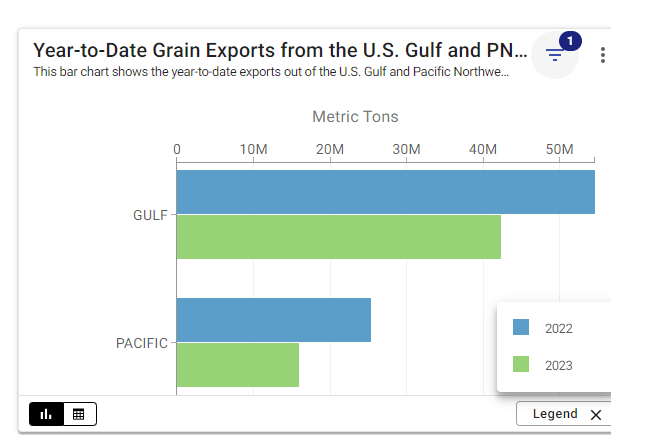
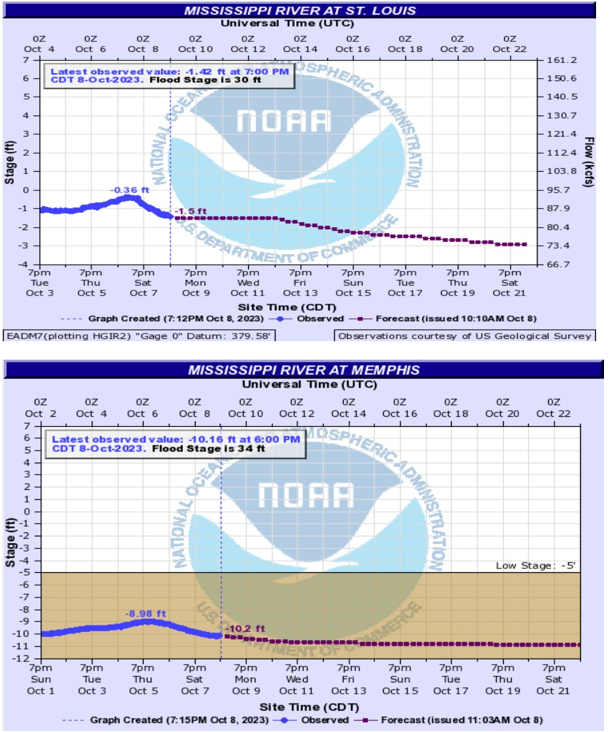
Xeneta, a data analytics firm specializing in shipping markets, has presented some data for their webinar January 25, 2024.
One of the most striking figures is the percentage of loads being shifted from negotiated contract rates to freight-all-kinds (FAK) rates. The latter are substantially higher in most cases and allow for additional accessory charges to be added.
One of those extra surcharges is for the risk associated with Red Sea transits. The Houthi attacks from Yemen have made sailing the Red Sea more dangerous, even though a consortium naval fleet is patrolling and has even hit Houthi positions in Yemen. There’s no question that insurance rates have increased for Red Sea transits.
These changes not only increase shipper cost, but also add to the volatility of load charges. Shippers have more trouble doing business when they can’t estimate their shipping costs precisely enough.
There’s also a fear that carriers are creating ‘artificial demand’, by blanking sailings. Discussions of a shortage of containers also lead shippers to book sooner than might be required. There’s not exactly a shortage. But changes to the routes are playing havoc with the ability to reposition containers. That means there could be a temporary shortage, and if a particular shipper is affected it creates a negative perception of the ocean carriers.
Freight forwarders are worried that this demand creation will pull forward shipments that could have been delivered later. There could be a large dropoff in business later in the year.
All this turmoil means shippers need to begin thinking about renegotiating contracts now before the season starts. There are many more moving parts to be discussed with the carriers.
Xeneta clearly hopes their data service will be chosen to aid in the negotiations. But the careful analysis provided should alert shippers, forwarders, and carriers to the instability and uncertainty in the pricing of ocean shipping services today.

ELOISA TOVEE FEBRUARY 01, 2024