Leaf Logistics, an innovative truckload freight platform, has a unique recipe for reducing unloaded miles and matching carriers with driver-friendly routes, called Flex Fleets. It coordinates truckload freight between shippers and logistics service providers (LSPs) like trucking firms and freight brokers. The concept is that LSPs act as dedicated carriers over a short time for packages of loads from different shippers, but on approximately the same route. The claim is that users can experience a 75% or more reduction in slack or empty travel time for trucks.
I interviewed Anshu Prasad, CEO of Leaf, for some perspective on how the new Flex Fleets system works. The essence is an analytical system that compiles load histories from all the shippers who sign up, projects them to the future, and builds blocks of future loads from one node to another. Leaf Logistics calls this a route.
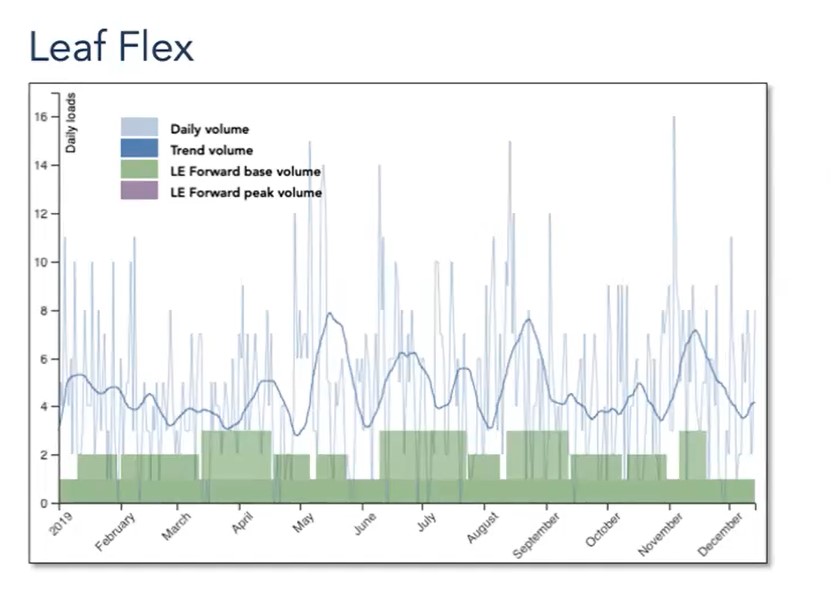
The image below shows the historical traffic by day on a specific route (think LA to PHX, for instance), with a moving average trend. The green bars display a way to ‘chunk’ the demand into blocks that would make attractive short-term contracts for a haulier. These are called Flex Contracts. Thus from about June 10 to July 15, there is a base volume of 3 loads a day to be handled by a dedicated contract.
That contract is much easier to digest for the LSP. It also assures shippers whose loads are in the block that there is a ‘dedicated’ resource to handle that base load. It’s much easier to create a Flex Contract; no long-term commitment, prices somewhere between spot and negotiated prices, and more flexibility for both parties. As you can see there’s a dip anticipated just after that block, and perhaps the shippers would not want 3 trucks per day available.
What’s in it for LSPs? Their alternative is to try selling dedicated services to many shippers to fill out schedules on a route, but there is a long sales cycle with each shipper, and some shippers would be bound to attract bids from others, breaking your grip. Traditional contracts are typically for longer periods, partly because they are hard to negotiate. And through Leaf, management is easier. Leaf estimates that an average of 20 or more ‘touches’ via EDI, email or calls can be reduced to under 5 using Flex.
Leaf’s Adapt data analysis constructs multi-shipper routes, and the LSP chooses a Flex Contract for such a route. The route can reduce unloaded miles and assure drivers they can fulfill them on time. It’s an advantage if an LSP wants to give drivers a ‘home life’. Quality of life is becoming an essential factor to keep drivers on board and happy. And eliminating unloaded miles and gaps in rolling service is huge; it’s the largest capacity loss in trucking logistics today.
Flex Fleets operates only with truckload (TL) shipments today, the largest segment of trucking. They have about 400 shippers enrolled; the shippers need to disclose historical data on their traffic lanes to Flex, though not to each other. Flex uses the traffic gathered to compute its route blocks. It’s a reasonable compromise with information that is not that useful for competition in reality. Flex is now in trials including reefer traffic.
Leaf usually enrolls the shippers’ preferred trucking vendors, so shippers do not need to worry about qualifying trucking firms again. The LSPs like it, because they get the Flex Fleets benefits of guaranteed loads in a workable pattern over a longer time horizon. Of course, all the carriers are insured. If something happens on a route, like an accident, weather, or carrier no-show, Leaf makes good on the route with a failover plan to ensure completion.
I asked Anshu if there was a plan to introduce Leaf’s concepts into container drayage, an area plagued with turnover, contracting issues, and driver exploitation. Anshu wants to test and refine the Flex concepts first before trying that difficult area. Drayage is an area with many owner-operators. The Leaf system does not have owner-operators as carriers. If one wants to participate, she could sign up with a trucker or broker who joins. Anshu says studies have shown that many full-truckload owner-operators work that way, possibly up to 70%.
Everyone benefits from the Flex Fleets idea to induce cooperative behavior on the part of shippers and LSPs. The shorter duration contract— a month to a year— with fewer conditions is easier to accept or say no to.
- Shippers benefit from dedicated and scalable capacity, without having to purchase or lease their own fleet — currently, they commit to fleets for years and have to pay for maintenance, regardless of utilization. Flex Fleets save shippers up to 30% on their line haul costs.
- Carriers benefit from consistent business and preferable freight, eliminating driver downtime and fleet empty miles — 40% of all trucks on the road today ride empty. Tender rejections drop from 30% to 0.
- Brokers benefit from enabling drivers to accurately predict their earnings, work from a preferred domicile, maximize their number of paid miles driven and return home each night for an improved quality of life on and off the road. For instance, Sage Freight has seen driver turnover drop from 75% to 15% or less on dedicated freight.
- Everyone benefits from reducing emissions by eliminating empty miles and delays. ESG ratings are improved in the fastest way for truckload haulage.
We have been saying for years that logistics is the only place in business where cooperation is routine. But in truckload, it hasn’t been. We need intelligent systems, like Leaf’s Flex Fleets, to identify how it can be made routine and easy.
Anshu indicates that he and his leadership team, some of whom worked together previously, have a long-term commitment to their business idea. That’s why they are growing deliberately with tested concepts, and why they have not sought large venture investments like many young logistics software firms. Instead, they want persistent solutions to the problem of cooperation that will capture the next-generation logistics information market.
And they’ll be helping truckers with some of their most intractable problems.

